In this chapter, we make a group and do some research about topic that he provides. Our topic is about "Communication and Multimedia (Technical Standards) Regulation 200)".
But in this post, i will not explain about malaysia regulation since i don't know about regulation in Malaysia. In this post, i will explain about CYBERLAW.
Cyberlaw is a term that encapsulates the legal issues related to use of communicative, transactional, and distributive aspects of networked information devices and technologies. It is less a distinct field of law in the way that property or contract are, as it is a domain covering many areas of law and regulation. Some leading topics include intellectual property, privacy, freedom of expression, and jurisdiction. (Resource).
Why computer crime is hard to define
1. Creating and changing laws are slow processes
2. Particular computer can be the subject, object or a medium of a crime. A computer can be attacked (attempted unauthorized access).
Digital Signature Act 1997
Why the Act exists
Transactions conducted via the Internet are increasing. As identities in cyberspace can be falsified and messages tampered with, there is a need for transacting parties to ascertain each other's identity and the integrity of the messages, thereby removing doubt and the possibility of fraud when conducting transactions online.
What the Act is about
The Act mainly provides for the licensing and regulation of Certification Authorities (CA). CAs issue Digital Signatures and will certify the identity (within certain limits) of a signor by issuing a certificate. The Act also makes a digital signature as legally valid and enforceable as a traditional signature. The Digital Signature Act was brought into force on 1st October 1998.
Computer Crime Act 1997
Why the Act exists:
As computing becomes more central to people's life and work, computers become both targets and tools of crime. This Act serves to ensure that misuse of computers is an offense.
What the Act is about
The Act makes it an offense to:
1. Enter or attempt to enter into computers and computer systems without authorization
2. Damage or alter data/information in computers or computer systems by planting viruses or other means
3. Aid people in doing items 1 & 2
4. Give passwords to people who are not authorized to receive it
The Computer Crimes Act was brought into force on 1st June 2000.
Telemedicine Act 1997
Why the Act exists
Healthcare systems and providers around the world are becoming interconnected. People and local healthcare providers can thus source quality healthcare advice and consultation from specialists from around the world, independent of geographical location. Conversely, interconnectivity also allows for non-quality healthcare advice and consultation from around the world. The Act serves to regulate the practice of teleconsultations in the medical profession.
What the Act is about
The Act provides that any registered doctor may practise "telemedicine" but other healthcare providers (such as a medical assistant, nurse or midwife) must first obtain a license to do so.
The Copyright (Amendment) Act 1997
Why the Act exists
Copyright serves to protect the expression of thoughts and ideas from unauthorized copying and/or alteration. With the convergence of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT), creative expression is now being captured and communicated in new forms (example: multimedia products, broadcast of movies over the Internet and cable TV). These new forms need protection.
What the Amendment Act is about
The Copyright (Amendment) Act amends the Copyright Act 1987 to extend copyright law to the new and converged multimedia environment. There is now clear protection accorded to multimedia works. The transmission of copyright works over the Internet now clearly amounts to infringement. Technological methods of ensuring works and authorship info are not altered or removed is also protected. The Copyright (Amendment) Act 1997 was brought into force on 1st April 1999.
The Communications and Multimedia Act 1998
Why the Act exists
Convergence of technologies is also resulting in the convergence of the following industries: telecommunications, broadcasting, computing and content. Previously, each of these industries was regulated by several different pieces of legislation (example: the Telecommunications Act 1950 and the Broadcasting Act 1988). The old regulatory framework cannot cope with convergence and inhibits the growth of the new converged industry.
What the Act is about
The CMA provides for a restructuring of the converged ICT industry. It creates a new system of licenses and defines the roles and responsibilities of those providing communication and multimedia services. Though intended to allow the converged ICT industry to be self-regulating, the Act also provides for the existence of the Communication and Multimedia Commission (the roles and powers of which are more clearly defined by the Communications and Multimedia Commission Act 1998) as a new regulatory authority to oversee the converged ICT industry. The Communications and Multimedia Act was brought into force on 1st April 1999.
Monday, October 26, 2009
Lec 10- CYBERLAW
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:37 AM 0 comments
Lec 9 - LEGAL AND ETHICAL ISSUES IN COMPUTER SECURITY
Legal & Ethical
*Law
*imply imposition by the obligation of obedience on the part of all subject to that authority
*Ethics
*a set of moral main beliefs or values
Categories of Law
*Tort law enables individuals to seek recourse against others in the event of physical, or financial injury.
*Civil law: represents a broad variety of laws that govern a nation or state
*Criminal law: addresses violations hurtful to society and is actively enforced through prosecution by the state
Differences between Laws and Ethics
LAW
*Interpreted by courts
*Enforceable by police and courts
ETHIC
*Personal choice
*Priority determined by individual if two principles conflict
Ethics Concept in Information Security
*Software License Infringement
*The lack of legal disincentives, the lack of punitive measures.
*criminal Use
*The low overall degree of tolerance for illicit system use may be a function of the easy association between the common crimes of breaking and entering of property to their computer-related counterparts.
*Three general categories of unethical and illegal behavior:
*Ignorance
*Accident
*Intent
Protecting Programs and Data
*Copyrights
*to cover works in the arts, literature and written scholarship
*Patents
*can protect a “new and useful process, machine, manufacture or composition of matter”
*Trade Secret
*must be kept a secret, trade secret protection can also vanish through reverse engineering
Open-source software affected by copyright protection. How?
*Subject to fair use
*Ease of filing
Information and The Law
*Legal Issues Related to Information
*electronic publishing
*Problem: How to ensure that the publisher receives fair compensation for the work?
*Database
*Problem: Difficult to determine that a set of data came from a particular database so that the database can claim compensation
*electronic commerce
*Problem: How to prove conditions of delivery
Rights of Employees and Employers
*ownership of a patent
* The person who owns under patent and copyright law is inventor (producer)
* ownership of a copyright
*Similar to ownership of a patent
Computer Crime
*A computer can be :
*Attacked, used as a means to commit crime
*Computer crime is hard to prosecute because:
*low computer literacy (lack of understanding), Lack of political impact
Ethical Issues in Computer Security
- Ethics & Religion
Distinguish ethics from religion, analyze a situation from an ethical perspective.
- Ethics is Not Universal
Ethics values is not universal, it varies by society within a society.
- Ethics Does Not Provide Answer
Ethical pluralism is recognizing that more than one position may be ethically justifiable.
Examining a Case for Ethical Issues
1. Understand the situation. Determine the issues involved.
2. Know several theories of ethical reasoning
3. List the ethical principles involved
4. Determine which principles outweigh others.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:35 AM 0 comments
Lec 8 - Wireless LAN Security
WEP use to provide comparable confidentiality to a traditional wired network in particular it does not protect users of the network from each other. WEP was supported by Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in 2003, and then by the full IEEE 802.11i standard (also known as WPA2) We can use Aircrack to hack wirelss.Hence, Aircrack is a set of tools for auditing wireless networks.
Wireless LANs
* IEEE ratified 802.11 in 1997- Also known as Wi-Fi.
* Wireless LAN at 1 Mbps & 2 Mbps. -WECA (Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance) promoted Interoperability.
* Now Wi-Fi Alliance 802.11 focuses on Layer 1 & Layer 2 of OSI model. -Physical layer Data link layer
802.11 Components
Two pieces of equipment defined:
* Wireless station A desktop or laptop PC or PDA with a wireless NIC.
* Access point A bridge between wireless and wired networks Composed of Radio Wired network interface (usually 802.3) Bridging software Aggregates access for multiple wireless stations to wired network.
802.11 modes
* Infrastructure mode
* Ad-hoc mode
There were 3 basic security for environment wifi :-
* Authentication – Provide security service to identify consumer identity communicate.
* Integrity – To be sure message unmodified during transaction between wifi clients and access point.
* Confidentiality – To provide privacy are achieved by a network wired.
WEP
* WEP stands for Wired Equivalent Privacy. This encryption standard was the original encryption standard for wireless. As its name implies, this standard was intended to make wireless networks as secure as wired networks.
WPA
* Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a software/firmware improvement over WEP. All regular WLAN-equipment that worked with WEP are able to be simply upgraded and no new equipment needs to be bought. WPA is a trimmed-down version of the 80.211i security standard that was developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance to replace WEP. The TKIP encryption algorithm was developed for WPA to provide improvements to WEP that could be fielded as firmware upgrades to existing 802.11 devices. The WPA profile also provides optional support for the AES-CCMP algorithm that is the preferred algorithm in 802.11i and WPA2.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:31 AM 0 comments
Lab 7 - SECURITY IN APPLICATIONS
Email has two part, header and body. Header part used to state the sender and email recipient. Body part is content of the message or email.
Security in email:
· Confidentiality
· Data origin authentication
· Message integrity
· Non-repudiation of origin
· Key management
MIME
Secure MIME is the new (proposed) Internet standard for secure email exchange, developed by RSA. It is not yet an official standard, but several vendors (including Netscape) already support S/MIME. It is probably the best long term solution, since it is an open Internet standard.
Typically is not necessary to make any modifications for S/MIME on the server. For instance with MS Exchange, it integrates into the exchange client via the MAPI interface.
Advantages:
1. It functions with both Eudora Pro 3.0 and Exchange (and can use the same certificates on the same machine).
2. No changes are required to the exchange server.
3. Certificates may either be self signed, or signed by a TTP such as
Disadvantages:
1. The user interface is not perfect, e.g. a user could easily unintentionally send an unencrypted email. The icons used to represent email don't seem to indicate if the received email was successfully decrypted and the signature checked. It is possible that these problems can be overcome by adding additional buttons to the toolbar, though this increases support costs.
2. When a signed message is received from someone for whom no certificate currently exists, the certificate is automatically added to the certificate database. Before this certificate can be used, it must be manually trusted. This procedure is a bit confusing for normal users, it should be handled by a nice pop-up box when the signed email is received.
PGP
PGP is a freeware and commercial email and file encryption utility. It is also discussed in the chapter "Security Mechanisms".
Secure Shell is a program to log into another computer over a network, to execute commands in a remote machine, and to move files from one machine to another. It provides strong authentication and secure communications over insecure channels. It is a replacement for rlogin, rsh, rcp, and rdist.
SSH
SSH protects a network from attacks such as IP spoofing, IP source routing, and DNS spoofing. An attacker who has managed to take over a network can only force ssh to disconnect. He or she cannot play back the traffic or hijack the connection when encryption is enabled.
When using ssh's slogin (instead of rlogin) the entire login session, including transmission of password, is encrypted; therefore it is almost impossible for an outsider to collect passwords.
Biometric
How Does Biometric Encryption Work?
Encryption is a mathematical process that helps to disguise the information contained in messages that is either transmitted or stored in a database, and there are three main factors that determine the security of any crypto system; the complexity of the mathematical process or algorithm, the length of the encryption key used to disguise the message, and safe storage of the key, known as key management.
The complexity of the algorithm is important because it directly correlates to how easy the process is to reverse engineer. One would think that this is the area of encryption that is the easiest to break, however most crypto systems are extremely well constructed and these are the least of the three factors that are vulnerable to attack.
The length of the encryption key used to disguise the message is the next important piece of the encryption process. The shorter the encryption key length, the more vulnerable the data is to a "brute force" attack. This term refers to an individual trying to improperly access data by trying all combinations of possible passwords that would allow access to the account. In non-biometric encryption processes such as passwords or PIN numbers, depending on the length of the key, the information may be vulnerable to access by unauthorized users. For example, a key that is three characters long would be much more prone to attack than one that is ten characters long because the number of possible permutations that must be run to find the right key are much higher in the key that contains ten characters. With current computer power, it is estimated that it would take four hundred years to find the right access combination for a sixty-four character key. Biometric encryption makes standard character encryption obsolete by replacing or supplementing the normal key characters with a personal identifier of the user that there can only be one perfect match for. Without this biometric key the information is inaccessible.
Safe storage of the key is the most vulnerable area in the encryption process. What would seem to be the easiest to manage becomes the most difficult because passwords or PINs can be lost or stolen. Good encryption keys are much too long for normal individuals to remember easily so they are usually stored on paper, smart cards, or diskette which makes them accessible to non-authorized users. Biometric encryption systems allow the user to transport the access key around without the need to make it vulnerable to be lost or stolen.
There are two broad categories of encryption systems; single key (symmetric) sytems and two key (public) systems. Symmetric systems utilize a single key for both the sender and receiver for the purpose of coding and decoding data. In 1972, IBM developed DES (Data Encryption Standard) which was adopted worldwide by 1977 as the most common single key system in the banking and financial sectors. The process of transmitting this type of key over such networks as the Internet is one of the major failures due to the vunerability of a single key system to interception. Electronic commerce requires that transactions be conducted over open networks instead of dedicated networks and single key systems do not offer a high enough level of security for such transmissions. This issue of security is why public key systems have been developed. Two-key systems use a public key to encrypt the data and a private key to decrypt the data. The public key systems allows better encryption than single key systems, however certification of the recipient of messages becomes an issue, which causes a hierarchy of certification to be developed resulting in a much slower processing time. Biometrics can aid in this process due to the inherent nature of using a physical trait of the desired recipient to decipher the message. It is this issue that has caused biometric encryption techniques to be valued for electronic commerce.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:30 AM 0 comments
Lec 6 - COMPUTER NETWORKS
A computer network is a group of computer that are connected to each other for the purpose of communication. Networks may be classified according to a wide variety of characteristics. This article provides a general overview of some types and categories and also presents the basic components of a network. (from: resource)
What is network can provide???
Basically, it is logical interface function. For example, sending message, receiving message, executing program, obtaining status information and other network users and their status.
And these are some terminology in networking that I'm sure, you guys that take IT for majoring in university already familiar of these: NODE, HOST, LINK, TOPOLOGY.
Network topologies
Tere are 4 thopology:
1. Bus Topology
To provide a single communication network on which any node can place information and from which any code can retrieve information. One attachment in bus terminology not impacts the other nodes.
2. Star topology
Has switch as a central. The central switch receives all messages, identifies the addresses, selects the link appropriate for that addresses and forwards the messages.
Image Hosted by UploadHouse.com
3. Ring Topology
To connect a sequence of nodes in a loop or ring. Can be implemented with minimum cabling.
4. Mesh Topology
Each node can conceptually be connected directly to each other node and routing logic can be used to select the most efficient route through multiple nodes.
Advantages in network computing
· Resource sharing is used to reduce maintenance and storage costs.
· Increased reliability means if one system fails users can shift to another.
· Distributing the workload means workload can be shifted from a heavily loaded system to an underutilized one.
· Expandability is system is easily expanded by adding new nodes.
Disadvantages in network computing
· Sharing, access controls for a single system may be inadequate.
· Complexity, a network may combine two or more systems with dissimilar operating systems with different mechanisms for interhost connection. Complexity of this nature makes the certification process extremely difficult.
· Unknown perimeter is one host may be a node on two or more different networks.
· Many points of attack, access controls on one machine preserves the secrecy of data on that processor. However, files stored in a remote network host may pass through many host machines to get to the user.
· Unknown path may be many paths from one host to another and users generally do not have control of how their messages are routed.
· Label formats differences is a problem which may occur in multilevel systems is that the access labels may have different formats since there is no standard
· Anonymity is attack can passed through many other hosts in an effort to disguise from where the attack originated
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:29 AM 0 comments
Lab 5 - Web Application
On this lab, we need to describe the flaw of web application and how it is exploited. Besides that, we also have to exploit the web vulnerabilities. After that, we need to list prevention method that can be taken to overcome web application vulnerabilities.
WHAT IS WEB APPLICATION SECURITY??
Web application or simply called webapp is an application that can be accessed using a web browser over a network, either the Internet or within the Local Area Network. It is developed using browser-supported language such as HTML, JavaScript, PHP, ASP and etc. The script produced is then rendered by common web browser. Web application let user to access application or system anywhere and at any time provided the user is connected to a network connection and there is a web browser installed on the machine. This ease of usage makes webapp popular among Internet user. Moreover the ability to update and maintain web applications without distributing and installing software on potentially thousands of client computers contribute to the popularity of the webapp. Nowadays webapp is used for accessing mail, online banking, online shopping, online reservation, wikis and many other functions.
An increase in the usage of web applications is directly related to an increase in the number of security incidents for them. Even though the server is patch with the latest version of the software, the network are installed with the latest firewall system and Intrusion detection system is deployed to monitor the network, if the web application itself is lack of security features the vital information stored in its content is still expose to intrusion. A Web application system should be carefully and safely develop because it is the first line of defense, any fault or flaws in it development stage, the server configuration and even the scripting used in it development can bring a major loop hole that can be manipulated by intruder to be used as the backdoor to the entire network.
Web Application
Web application is an application that can be accessed using a web browser over a network. It is developed using browser-supported language such as HTML, JavaScript, PHP, ASP and etc. We also can use software such as dreamweaver to create a web application. The script produced is then rendered by common web browser. User can access web application anywhere and at any time, but user need to connect to a network connection and there is a web browser installed on the machine. This ease of usage makes web application popular among
internet user. Moreover the ability to update and maintain web applications without distributing and installing software on potentially thousands of client computers contribute to the popularity of the webapp. Nowadays webapp is used for accessing mail, online banking, online shopping, online reservation, wikis and many other functions.
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is an open community that focuses on improving the security of application software. Anyone can join this community and contribute an idea for developing secure software. OWASP provide free material such as article on secure programming, security testing guide and much more but all of the material is under free software license.
WebGoat
WebGoat is simulation toolkit used to demonstrate how we can exploit the vulnerabilities of a poorly design web application. WebGoat provide hints and code to fexploit the vulnerabilities. WebGoat will keep track on the progress of the user on every lesson they completed, user can see their level of competence in trying to solve every problem given in the lesson.The primary goal of the WebGoat project is simple, to create a de-facto interactive teaching environment for web application security.
WebScarab
WebScarab is another tool to expose the working of an HTTP(S) based application, whether to allow the developer to debug otherwise difficult problems, or to allow a security specialist to identify vulnerabilities in the way that application has been designed or implemented. WebScarab can use in any platform because it developed use JAVA programming language. WebScarab can intercept HTTP and HTTPS communication.
WebGoat and WebScarab
WebGoat = Simulation toolkit used to demonstrate how we can exploit the vulnerabilities of a poorly design web application.
WebScarab = Tool for everyone who need to expose the working of an HTTP(S) based application, whether to allow the developer to debug otherwise difficult problems, or to allow a security specialist to identify vulnerabilities in the way that application has been designed or implemented.
Web Application Hacking simulation using WebGoat and WebScarab
Step 1: Copy the WebGoat-OWASP_Standard-5.2.zip and extract it to the C:\ drive.
Step 2: Open the C:\ WebGoat-5.2 folder and open the webgoat.bat to start the apache tomcat J2EE.
Step 3:Open an IE 6.0 web browser or a firefox web browser and type http://localhost/WebGoat/attack.
Step 4: Login as User Name: guest Password: guest
Step 5: Open webscarab-selfcontained-20070504-1631.jar
Step 6: If the WebScarab does not open do install the JDK module (jdk-6u4-windows-i586-p.exe) to your computer.
Step 7: Once the WebScarab started
Step 8: Next Configure the Web browser proxy starting so that it listen to 127.0.0.1 (localhost) port 8008.
Step 9: Go to WebScarab and click on the intercept tab and enable the intercept request checkbox but disable the intercept response checkbox. This will enable the intercept features of the WebScarab in which it will intercept any request signal from the web browser.
Step 10: Close your previous web browser, open it again and type in http://localhost/WebGoat/attack.
Step 11: WebScarab will intercept your request to visit the website by prompting an Edit request window as depicted in figure 5.6. This prompted window shows the request data that you send to the web server.
Step12: The text field indicated by the arrow shows the text field containing the data you send to the web server and it can be modified.(in some of the following task you need to modified the content of the text field to help you solve the problem in lesson.
Step13: For this task do not changes the text field value just click the [Accept changes] button to view the WebGoat main page.
Step 14: Each time you click on a submit button or a link on the webpage, the Edit request window will always appear, so make sure you click on Accept changes button to view your request page display on the browser.
Getting started with WebGoat and WebScarab
Step 1: Click on [Start WebGoat]
Step 2: Click on the Introduction | How to work with WebGoat menu.
Step 3: Read and follow the instruction given in the WebGoat.
XSS Attack
Step 1: Click on the Cross Site Scripting (XSS) | Phising with XSS menu
Step 2: Apply the script below to the text field in order to create a false login page so that you can harvest the username and password keyed in by the user.
Step 3: Once you hit the Search button you will see a comment page containing a place for you to login. This login page is created using the java script above.
Step 4: Try login in with any username and password; if this is a real phishing website you would not get the prompted message on your screen but the value you supplied might be send across the world to a server that gather the login information.
Step 5: Next click on the Cross Site Scripting (XSS) | Reflected XSS Attacks menu.
Step 6: In this lesson some prevention mechanism has been build in the script, some field have a validation toward the character you supplied. It will reject any tag symbol you used, however there are still some that is not protected. By using the script below find which the text field that can be exploited using XSS attack?
Injection Flaws
Step 1: Click on the Injection Flaws | Numeric SQL Injection menu.
Step 2: From the combo list choose a weather station and click the [Go!] button, (Do not forget to click on the accept changes button of the edit request windows) you will get the information for the country you select.
Step 3: To apply the Injection flaws you need to choose a new country and click [Go!] button. Before clicking the [Accept changes] button on the edit request windows, in the [URLEncoded] tab, add the value station variable with
This is input is a numerical value
Step 4: Once the value is changed, click [Accept changes] button. The entire data is displayed on the screen. This shows that by manipulating the input field that is not properly design we can display the entire data in the database.
Step 5: Repeat this task on the Injection Flaws | String SQL Injection. Use the right input for this problem and compare the result. (Hint: The input should be a string).
Malicious File Execution
Step 1: Click on the Injection Flaws | Command Injection menu.
Step2: By choosing the lesson plan to view and clicking on [View] button, user will be shown the content of the lesson. This exercise will manipulate the input field by adding the input with a command line instruction.
Step 3: Select a new lesson and click [View]. Before clicking the [Accept changes] button add the following command to your HelpFile variable value
This command will display directory list and network configuration setup.
Step 4: Once you click the [Accept changes] button the following output will be displayed on the screen.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:29 AM 0 comments
Lec 5 - Database Security
Databases need to have level of security in order to protect the database against both malicious and accidental threats. A threat is any type of situation that will adversely affect the database system. Some factors that drive the need for security are as follows:
- Theft and fraud
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Privacy
- Database availability
Threats to database security can come from many sources. People are a substantial source of database threats. Different types of people can pose different threats. Users can gain unauthorised access through the use of another person's account. Some users may act as hackers and/or create viruses to adversely affect the performance of the system. Programmers can also pose similar threats. The Database Administrator can also cause problems by not imposing an adequate security policy.
Some threats related to the hardware of the system are as follows:
- Equipment failure
- Deliberate equipment damage (e.g. arson, bombs)
- Accidental / unforeseen equipment damage (e.g. fire, flood)
- Power failure
- Equipment theft
Threats can exist over the communication networks that an organisation uses. Techniques such as wire tapping, cable disruption (cutting / disconnecting), and electronic interference can all be used to disrupt services or reveal private information.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:28 AM 0 comments
Lab 4 - Cryptography Extended
Cryptography Extended
In this lab we learn that cryptography algorithm can be classified into two categories, symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric is using same key to encrypted and decrypted the plain text whereas asymmetric using different key to encrypted and decrypted plain text.
Symmetric can divide to:
1. Substitute encryption
· In substitute encryption, character in plain text being substitute with another character. Each character can be substitute with one character or multiple characters. Caesar cipher is example of substitute with one character and Vigenere cipher is example of substitute with multiple characters. Caesar cipher is easy to break by using brute force attack; an attacker can easily try every combinations of character to break the code as the numbers of possibility is 26. Vigenere cipher is an improvement from Caesar cipher.
2. Transposition encryption
· This method is change the location of characters or reordering the character in plain text. The first character in plain text might be placed on fifth position and fifth character might be placed in another location in plain text.
Asymmetric encryption involves two key in encryption and decryption. The encryption key is called public key and decryption key called private or secret key. These algorithms allow the public key to be publicized, which means people with the public key can encrypt the plain text and the proper recipient with the private key can decrypt the plain text. To produce this to key used RSA algorithm. RSA is founded by Rivest, Shamir and Adleman of MIT in 1977.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:28 AM 0 comments
Lec 4 - Protection in Operating Systems
AUTHENTICATION
* Verification of identity of someone who generated some data.
* Relates to identity verification.
*
classifications of identity verification:
#by something known e.g. password
#by something possessed e.g. smart card, passport
#by physical characteristics (biometrics) e.g. finger prints, palm prints, retina, voice
#by a result of involuntary action : signature
*
Requirements – must be able to verify that:
¤Message came from apparent source or author
¤Contents have not been altered
¤Sometimes, it was sent at a certain time or sequence
*
Protection against active attack (falsification of data and transactions)
PASSWORD
¨Protection of passwords
¤Don’t keep your password to anybody
¤Don’t write or login your password at everywhere
¤Etc.
¨Choosing a good password
¤Criteria:
-Hard to guess and easy to remember
¤Characteristics of a good password
-Not shorter than six characters
-Not patterns from the keyboard
-Etc.
¨Calculations on password
¤Password population, N =rs
¤Probability of guessing a password = 1/N
¤Probability of success, P=nt/N
***Support for password compliance reporting and strong authentication
-OneSign gives organizations a variety of powerful tools for password authentication, including:
*Automated password generation and changes, including the ability to generate strong random passwords on behalf of end-users.
*Self-service password reset - enabling users to securely reset their own passwords.
*Password authentication policy implementation.
*Built-in support for strong authentication options such as fingerprint biometrics, smart cards. proximity cards, USB tokens, and more.
*Pre-built and customized reports that track password authentication and access and provide data on who accessed what, how, when, and from where
*Audit logs of access and password change activity, delivering the information IT departments need to enhance and enforce compliance across the enterprise.
*Support for end-user workflow including shared workstations and fast user switching.
***Techniques for guessing passwords***
-Try default passwords.
-Try all short words, 1 to 3 characters long.
-Try all the words in an electronic dictionary(60,000).
-Collect information about the user’s hobbies, family names, birthday, etc.
-Try user’s phone number, social security number, street address, etc.
-Try all license plate numbers
-Use a Trojan horse
-Tap the line between a remote user and the host system.
BIOMETRIC
¨The term is derived from the Greek words bio (= life) and metric (= to measure)
¨Biometrics is the measurement and statistical analysis of biological data
¨In IT, biometrics refers to technologies for measuring and analysing human body characteristics for authentication purposes
¨Definition by Biometrics Consortium – automatically recognising a person using distinguishing traits
#How does it works?
¨Each person is unique
¨What are the distinguishing traits that make each person unique?
¨How can these traits be measured?
¨How different are the measurements of these distinguishing traits for different people
#Biometric Technologies
¤Fingerprint biometrics – fingerprint recognition
¤Eye biometrics – iris and retinal scanning
¤Face biometrics – face recognition using visible or infrared light (called facial thermography)
¤Hand geometry biometrics – also finger geometry
¤Signature biometrics – signature recognition
¤Voice biometrics – speaker recognition
#Classification of biometric methods
¨Static
¤Fingerprint recognition
¤Retinal scan
¤Iris scan
¤Hand geometry
¨Dynamic
¤Signature recognition
¤Speaker recognition
¤Keystroke dynamics
#Biometric system architecture
¤Data collection
¤Signal processing
¤Matching
¤Decision
¤Storage
¤Transmission
ACCES CONTROL
¨“The prevention of unauthorized use of a resource, including the prevention of use of a resource in an unauthorized manner“
¤central element of computer security
¤assume have users and groups
nauthenticate to systemassigned access rights to certain resources on system
Requirements
¨reliable input
¨fine and coarse specifications
¨least privilege
¨separation of duty
¨open and closed policies
¨policy combinations, conflict resolution
¨administrative policies
Elements
¨subject - entity that can access objects
¤a process representing user/application
¤often have 3 classes: owner, group, world
¨• object - access controlled resource
¤e.g. files, directories, records, programs etc
¤number/type depend on environment
¨• access right - way in which subject accesses an object
¤e.g. read, write, execute, delete, create, search
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:26 AM 0 comments
Lab 3 - Authentication and Basic Cryptography
During this lab, we will implement the Caesar Cipher and Vigenere Cipher for Symmetric Cryptography.
As in the previous lecture, we already know that cryptography is divided into 2 main categories which is symmetric and asymmetric. In symmetric encipherment, plaintext is encrypted and decrypts using the same key whereas asymmetric encipherment is using different keys to encrypt and decrypt a plaintext.
Below is an example of symmetric encipherment using Caesar Cipher
The Caesar Cipher is formed by shifting the letters of the original alphabet. For example by replacing each letter of the alphabet with the letter three places down the alphabet. It is monoalphabetic as only one letter in plaintext is exchanged for one letter of ciphertext.
Plaintext alphabet A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Ciphertext key D E F G H I J KLM NO P Q RS T U V W X Y Z A B C
A caesar cipher with a key 3
For an example the plain text below can be encrypted using key 3 to get the cipher text
THE ATTACK TONIGHT START AT EIGHT, REGROUP AT STATION A
Plaintext
WKHDWWDFNWRQLJKWVWDUWDWHLJKWUHJURXSDWVWDWLRQD
Ciphertext
Example of symmetric cryptography using Vigenere Cipher
Vigenere table
The cipher text encrypted using Caesar cipher method is easily broken by using a brute force attack. An attacker can easily try every combinations of character to break the code as the number of possibility is just 26. In order to improve the deciphering process we can used the vigeneré cipher method. The Vigenère cipher is a method of encrypting alphabetic text by using a series of different Caesar ciphers based on the letters of a keyword. It is a simple form of polyalphabetic substitution. You can refer to the Vigenere table for making it easier to encrypt a plaintext using this method.
A key is needed to encrypt a plaintext; a key can be a word or a phrase. To have a strong cipher text it is advised to use different key on each encryption. This will prevent from a brute force attack on a second message if the first message has been intercepted.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:26 AM 0 comments
Lec 3 - Program Security
There are 2 type of Vulnerabilities :-
1. Secure Program
2. Malicious Code
Secure Program
* An assessment of security can also be influenced by someone’s general perspective on software quality. For example, if your manager’s idea of quality is conformance to specifications, then she might consider the code secure if it meets security requirements, whether or not the requirements are complete or correct. This security view played a role when a major computer manufacturer delivered all its machines with keyed locks, since a keyed lock was written in the requirements. But the machines were not secure, because all locks were configured to use the same key! Thus, another view of security is fitness for purpose; in this view, the manufacturer clearly had room for improvement.
Malicious Code
* Malicious code (also called vandals) is a new breed of Internet threat that cannot be efficiently controlled by conventional antivirus software alone. In contrast to viruses that require a user to execute a program in order to cause damage, vandals are auto-executable applications.
Malicious code can take the form of:
* Java Applets
* ActiveX Controls
* Scripting languages
* Browser plug-ins
* Pushed content
- Once inside your network or workstation malicious code can enter network drives and propagate. They can also cause network and mail server overload by sending email messages, stealing data and passwords, deleting document files, email files or passwords, and even re-formatting hard drives.
Examples of malicious codes:
* Trojan Horse – a program which performs a useful function, but also performs an unexpected action as well.
* Virus – a code segment which replicates by attaching copies to existing executables.
* Worm – a program which replicates itself and causes execution of the new copy.
* Logic bomb – malicious code that activates on an event (e.g., date).
* Trap Door (or Back Door) – undocumented entry point written into code for debugging that can allow unwanted users.
Viruses
* A program or piece of code that is loaded onto your computer without your knowledge and runs against your wishes. Viruses can also replicate themselves. All computer viruses are manmade. A simple virus that can make a copy of itself over and over again is relatively easy to produce. Even such a simple virus is dangerous because it will quickly use all available memory and bring the system to a halt. An even more dangerous type of virus is one capable of transmitting itself across networks and bypassing security systems.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:24 AM 0 comments
Friday, October 16, 2009
Sahabat
Salam perjuangan... 2 3 hari nie rasa x sedap hati... mudah sngat terasa... mungkin terlalu sibuk dengan project, bengkel tambahan pulak exam dah hampir... masalah keluarga, sahabat... Harap Allah kuatkan hati ini utk tepuh ujian dunia yang sementara...
dakwah+perjuangan +study....
Terbuka fikiran bila td ym ngan sahabat dari bumi madinah...
Tersedar bahawa method dakwah perlu disesuaikan mengikut persekitaran dan kategori sasaran, agar penyampaian berkesan... Ada kisah yang boleh membuatkan keegoaan seseorang luntur yang kita sering dengar melalui pembacaan kita,Usrah,kuliah, dan sebagainya..Ceritanya bermula.....Begini...
Suatu ketika Ahmad dan Ali(Bukan nama sebenar) bermusafir ke satu perjalanan yang jauh. tiba2 Ahmad dan ali bertengkar untuk menentukan jalan yang patut dilalui... nyata kesilapan Ahmad,ttp saling salah menyalahi antara 1 sama laen, sehingga membuatkan mereka tersesat jauh..Akhirnya PAAAANGGGG......aLI menampar Ahmad kerana tertekan .. Tiba di perhentian, Ahmad terus menulis "HARI INI SAHABATKU MENAMPAR KU"... diatas pasir..
Mereka meneruskan perjalanan, Tiba di tepian pantai, laut bagai memanggil mereka untuk mandi kerana cuaca yang agak panas membuatkan badan mereka tidak selesa. AHMAD bersedia untuk mandi, Hampir 20minit...TIBA2..AHMAD hampir lemas..Segera Ali berlari dari permukaan air bagi mendapatkan Ahmad yang jauhnya hampir 200m darinya..Bantuan pernafasan segera dilakukan,AHMAD berjaya di selamatkan..
AHMAD segera mengukir sesuatu pada batu yang berhampiran dan menulis..."HARI INI SAHABATKU MENYELAMATKAN NYAWAKU.."
Ali merasa pelik dengan tindakan AHMAD...Lantas Ali bertanya apa yang kau lakukan? apa motif sebenar pasir dan batu?
Lantas AHMAD menjawab..." Tika sahabat melukai hati kita,kita harus menulisnya pada pasir kerana Angin Kemaafan mudah menghapuskan tulisan..Dan pabila sahabat kita berbuat sesuatu kebaikan, aku pahatkan pada batu agar tetap dikenang dan tidak hilang ditiup waktu... Sahabat..
Aku mencintaimu kerna Rasulullah memerintahkan aku mencintaimu. Ya,tidak beriman seseorang itu sehingga dia mencintai saudaranya sepertimana dia mencintai dirinya sendiri.
Sahabatku yang sangat aku cintai..
Sungguh,jalan yang kita lalui ini bukan jalan yang indah dan mudah. Jalan ini matlamatnya cantik dan mengkagumkan.Tapi, sungguh tidak dapat aku janjikan kepadamu jalan ini akan senang kau lalui. Bukankah sejarah membuktikannya, haq yang ingin dibawa tentu sekali akan ditentang.
Sahabat..
Bukankah dalam kita berdiskusi, seringkali kita ingatkan pejuang yang telah lama terkorban dulu? Sheikh Hassan Al Banna,ditembak di pasar. Kerna apa? Kerna dia membawa yang haq! Syed Qutb,nyawanya tercabut menemui Rabb nya di tiang gantung? Kerna apa? Kerna dia membawa yang haq. Sheikh Ahmad Yassin dibunuh dengan misil yahudi laknatullah di hadapan masjid di subuh yang hening. Kerna apa? Kerna dia juga membawa yang haq!
Amanah ini untuk kita,sahabatku.Amanah ini untuk orang seperti kalian. Bukanlah aku ingin menggoyahkan semangat wajamu dan bahkan tidak sesekali. Tetapi sahabat,yang pasti ingin aku ingatkan janji Allah terhadap orang yang menolong agamanya, Allah pasti akan membantu urusannya. Aku ingin ingatkanmu kasih sayangNya dan rahmatNya terhadap hamba yang diredhai Nya. Bukankah senang nanti bila Allah tanyakan kepada kita: Apa yang kau gunakan masa mudamu dan aku dan kau serentak menjawab :Ya Tuhanku, Ya Rabb, masa mudaku dan masa tuaku adalah aku letakkan pada jalanMu. Adalah untuk Kau. Hanya untuk hidup dalam redhaMu walau kami ditekan. Untuk hidup dalam cinta kami kepada Mu.
Sahabat...
Peluru, tali gantung, pedang yang tajam, bahkan tekanan yang kuat dari pengalaman kehidupan sememangnya boleh melemahkan sesiapa sahaja. Tapi bukan engkau. Engkau dibina dengan tarbiyah. Dihiasi keindahan akhlak. Dilahirkan sebagai pendukung agama ini. Biar siapa sahaja pun engkau, biar apa sahaja kata orang,kau terus menguatkan langkah menyusur jalan in. Aku yakin,kerna kau sahabatku.
Sahabatku yang dikasihi..
Tidak dapat aku janjikan kesenangan dan kemewahan mengikut jalan ini. Tidak dapat aku berikan nama dan pangkat. Tapi akan ku tawarkan yang lebih baik dari segala itu. Akan kuberikan doaku semoga kau teguh dalam jalan ini .Akan ku bersama kau melangkah membawa haq dalam jalan ini. Akan aku luka dan berdarah bersama kau. Kerna kita saudara yang saling mencintai kerna Nya. Andai aku ada menyakiti kalian aku mohon dimaafkan, andai aku tersala arah dan langkah, aku pohon petunjuk dari kalian...
TERIMA KASIH SAHABAT...
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 6:21 AM 0 comments
Tarik Nafasmu Sedalamnya
بســـــــــم الله الرحمان الرحيم
الحمد لله رب العالمين حمداً يوافى نعمه ويكافئ مزيده
اللهم صل على نور الأنور وسر الأسرار وترياق الأغيار
ومفتاح باب اليسار سيدنا و مولانا محمد المختار
وآله الأطهار وأصحابه الأخيار عدد نعم الله وأفضاله
- Selawat asy-Syeikh Ahmad al-Badawi / Selawat Nur / Selawat Anwaar dan Asror
اللهم صلي وسلم على سيدنا ونبينا محمد الكريم وعلى آله وصحبه اجمعن
Salam persaudaraan! Tarik nafasmu dalam-dalam kemudian duduk diam seketika, atau mungkin boleh saja kau pejamkan mata. Gelap! Dalam keadaan gelap-gelita itulah kau cuba nyalakan cahaya, atau dalam keadaan begitu kau bergerak saja menggunakan mata hati, kerana mata hati sebenarnya mampu menembusi apa saja.
Apa yang kita ingini dalam hidup ini sebenarnya? Hidup dan kehidupan bagaimana yang kita dambakan? Jawapan mudahnya, semua orang mahu senang! Mahu apa saja yang diingininya, apa saja yang diidamkan dan diimpikannya dapat dipenuhi tanpa bersusah-payah.
Tarik nafasmu dalam-dalam dan pejamkan mata! Dalam kegelapan itu kau tanyakanlah kepada diri sendiri, adakah kehidupan yang sebegitu mudah?
Kau mungkin ingin sekali memberikan jawapan 'YA', atas dasar apa yang kau lihat di sekelilingmu. Benarkah apa yang kau lihat itu sebagai sebuah realiti? Atau ia hanya sebuah bayangan indah yang
telah mengaburi pandangan matamu, yang mengelabui mata hatimu? Kau pasti akan termenung seketika kerana celaru mencari jawapan hakiki. Lalu kau akan berada buat beberapa ketika dalam lingkungan dunia tak pasti.
Kau ingin hidup bahagia, dengan memiliki segala apa yang indah, yang sempat singgah di mindamu. Soalan mudah - Siapa yang tak ingin kehidupan begitu? Rasanya tak ada seorang pun yang mahu menolak kehidupan mewah, kerana kita sekalian hamba ini memang sentiasa bernafsu dan berselera untuk bersenang-lenang.
Bagaimana pun, nasib di antara kita sekalian hamba ini tidak sama. Takdir untuk kita setiap hamba ini tak serupa. Kerana, Maha Pencipta itu Maha Mengetahui tentang apa yang dicipta-Nya. Maha Mengetahui tentang segala sebab dan akibat terhadap kita sekalian hamba ini. Hanya kita hamba ini saja yang tidak berapa mahu ambil tahu, walaupun telah diberitahu tentang segala apa yang patut diketahui.
Kenapa nasibku begini? Malang sunyi, sentiasa dilanda kecewa dan Ahh, sebuah keluhan dilepaskan. Adakah ini bunyi sebuah keluhan seorang hamba yang tak pandai bersyukur? Adakah ini keluh-kesah seorang hamba yang putus asa dengan hidupnya? Adakah ini rintihan dan ratapan seorang hamba yang tidak redha terhadap ketentuan Maha Pencipta? Segalanya mungkin, dan kemungkinannya juga ungkapan seperti ini pernah kita lafazkan!
Soalnya kenapa? Jawabnya, kerana apa kita hamba ini diciptakan oleh Maha Pencipta. Kita sekalian hamba ini boleh saja melontarkan sejuta satu persoalan, tapi sedarkah kita bahawa segala jawapan telahpun tersedia. Cuma, kita hamba ini saja yang buta! Yang melihat dengan mata, tapi tak nampak satu apa benda!
Kita hamba ini mahukan bahagia sepanjang masa, tapi kenapa pula dihadiahkan dengan derita? Tarik nafasmu dalam-dalam kemudian pejamkan mata apabila kau menyedari bahawa ketika ini kau berdiri di atas muka bumi yang tiada kekalnya, maka kau akan mampu mencari jawapannya. Kita sekalian hamba ini dihantar menghuni dunia untuk diduga. Maha Pencipta sudah berjanji tentang imbuhan-imbuhan yang akan diberi-Nya. Namun, percumakah segalanya? Kita harus buktikan kesetiaan, kita harus tunjuk sifat kehambaan kepada Sang Pencipta Yang Maha Berkuasa.
Hidup dan kehidupan ini sering kita gambarkan sebagai indah. Tahukah kau bagaimana keindahan sebenar dalam hidup dan kehidupan ini? Cukupkah kau gambarkannya dengan memiliki harta menimbun sebagai hidup yang indah? Bukan! Bukan itu dan bukan di situ indahnya!
Sesuatu yang indah mesti seimbang dan mempunyai imbangan - Ada Pro ada Kontra. Makanya, kehidupan yang indah adalah apabila kebahagian itu disulami dengan derita - sebagai sebuah sentuhan hikmat agar kita tak alpha untuk selamanya. Kita perlu merasa duka setelah kita diberi kegembiraan - Agar kita tak terus ketawa sampai tak ingat dunia! Bukankah dalam hidup dan kehidupan ini segalanya berpasang-pasangan? Jadi, keindahan dalam hidup itu berlaku apabila kita mampu melengkapkan setiap pasangannya.
Namun, hakikat kita hamba ini lain benar mahunya. Mahu senang, mahu ketawa, mahu gembira sepanjang masa! Jika begitu yang sering kau fikirkan, tarik nafasmu dalam-dalam kemudian pejamkan mata. Pertama-tama, ingatlah bahawa kau kini berpijak di alam fana bukannya di syurga! Kehidupan alam fana inilah nanti yang menentukan kehidupan kekalmu.
Untuk kesekian kalinya tarik nafasmu dalam-dalam sebelum nanti kau tidak akan bernafas lagi, kemudian pejamkan matamu rapat-rapat sebelum ia terpejam selamanya lalu, tidakkah kau syukuri dengan apa yang telah diberi-Nya selama ini?
Jangan kau ratapi nasib sendiri,
Jangan kau tangisi kehilangan yang dialami,
Syukur atas apa yang diberi,
Redha dengan apa anugerah ilahi.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 1:51 AM 0 comments
Wanita : Menurut Syeikh Said Badiuzzaman An-Nursi

Wanita...lembut dalam pandangan mata...tapi bisa menggugat isi dunia"
"Wanita...kerananya lelaki menerobos tembok besi, gagah menjulang risalah Nabi.... Wanita...kerananya lelaki terjerumus ke lembah kibir firauni, melapah manusiawi..."
Said Nursi pernah menceritakan, betapa pentingnya seorang perempuan. Hinggakan dikhususkan sebuah risalah di dalam Rasail al-Nur bertajuk "Murshid al-Akhawaat". Penghargaan Nursi terhadap bondanya sangat tinggi. Bonda Nursi bernama Nurriyye.
Nursi menukilkan, segala ilmu dan kelebihan yang dimilikinya adalah berpunca daripada bazrah (benih) yang telah disemai oleh bondanya itu. Tanpa bondanya menyemai benih yang baik sejak kecil, mana mungkin hatinya cenderung untuk berada di lebuhraya yang terus menghala ke akhirat ini. Faktor primernya adalah asuhan dan didikan bondanya yang sungguh tinggi taqwa dan wara'nya. Guru-guru dan masyaikhnya pula bertanggungjawab menyuburkan benih hasil semaian bondanya itu. Tapak kukuh dibina oleh bondanya Nursi sendiri, tidak orang lain.
Semasa Nursi masih kecil, kelebihannya begitu terserlah di kalangan teman sebaya malah yang lebih besar dibanding Nursi. Kelebihan Nursi terserlah dari sudut kecerdasan dalam pelajaran, mahupun kekuatan fizikalnya. Gurunya pernah menziarahi keluarga Nursi untuk melihat faktor yang membentuk peribadi unik Nursi ini. Masya Allah...kawan-kawan nak tahu, bila ditanya pada Nurriyye bonda Nursi itu, apakah rahsia di sebalik kelebihan anak-anaknya itu? Nurriyye penuh tawadhuk menjelaskan, "saya tidak meninggalkan solat malam sejak dahulu, kecuali ketika uzur syar'ie...dan saya tidak akan menyusukan anak-anak tanpa ada wudhuk"
Tahulah gurunya...tidak mustahil ibu seperti ini, akan melahirkan anak seperti Nursi. Ketaqwaan dan kewara'an ayahanda Nursi juga tidak terkecuali. Ayahandanya yang dikenali sebagai Sufi Mirza tidak akan memberi makan keluarganya dari sebarang unsur syubahat. Hatta ternakannya dipastikan tidak memakan rumput-rumput milik orang lain, beliau akan mengikat mulut lembu-lembunya sehingga sampai di ladangnya sendiri baru dilepaskan. Ini semata-mata, memastikan hasil susu dan daging yang akan dijamu pada keluarganya tidak tercemar dengan harta orang lain. Masya Allah, Tabarakallah.
Sejak berusia, sembilan tahun, Nursi telah terpisah dari bondanya. Ketika mendengar berita bondanya telah kembali ke rahmatullah, menangislah Nursi yang ketika itu dalam buangan jauh sama sekali dari keluarga dan kampung halaman. Pemergian bondanya diumpakan seolah hilanglah separuh dari dunianya...Ya Baqi, Anta al-Baqi, Ya Baqi, Anta al-Baqi.. Hasbunallahhu wa ni'mal wakil, ni'mal mawla wa ni'man nasir.
Nursi sangat menghargai makhluk yang bergelar perempuan. Beliau mengingatkan makhluk yang begitu cantik kejadiannya ini supaya tidak sampai menjadi bidadari Jahannam. Lantaran tenggelam dalam arus dunia yang penuh tipu daya. Mempergunakan segala kelebihan kurniaan Allah untuk merosakkan lelaki dan membawa fitnah dahsyat di akhir zaman. Hati-hatilah wahai wanita...
Nursi mempertegaskan, wanita adalah hulubalang atau perwira kepada tajalli sifat Jamal Allah. Wanita adalah hero kepada sifat rahmah, ra'fah, hanan dan syafaqah. Sifat-sifat ini guna untuk mendidik keluarga, suami dan anak-anak. Bukan guna buat merosak lelaki. Bukan pula memburu persamaan hak. Lelaki dan perempuan punya tanggungjawab yang berbeza, sebab itu dikurnia fisiologi dan psikologi yang juga berbeza. Lelaki dan perempuan tidak pernah ada persaingan atau perlumbaan dalam dunia ini, kerana tidak akan ada sesiapa yang menang. Dua makhluk ini tidak perlu bersaing sama sekali, malah perlu lengkap melengkapkan. Allah menjadikan lelaki dan perempuan adalah untuk saling menyempurnakan. Masing-masing punya tugas dan tanggungjawab. Masing-masing punya taklif.
Petikan:
http://albazrah.blogspot.com/2006/05/perempuan-di-hati-nursi.html
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 12:59 AM 0 comments
Thursday, October 15, 2009
ذکرالله
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
اللهم صل على سيدنا محمد عبدك
ورسولك النبي الأمي
وعلى آله وصحبه وسلم
- Selawat Ummi
اللهم أنت ربي لا إله إلا أنت خلقتني و أنا عبدك
وأنا على عهدك ووعدك ما استطعت
أعوذ بك من شر ما صنعت
أبوء لك بنعمتك على و أبوء لك بذنبي
فاغفر لي فإنه لا يغفر الذنوب إلا أنت
- Sayyidul Istighfar
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 5:36 AM 0 comments
Merindukan Allah
السلام عليكم و رحمة الله و بركاته
Ketika malam telah larut, alam fikiranku melayang mengembara kearah kegelapan malam, fikiranku menerawang kesebuah kuburan yang kaku, gundukan tanah merah yang dingin, perut bumi yang menjadi kediamanku kelak, didalamnya tak lain cacing dan serangga pemakan bangkai, tubuhku yang tak mampu menepis binatang yang menggerogotiku dan menjadikan tubuhku sarang dan tempat bertelur, alangkah tak berdayanya tubuh ini, sahabatku meninggalkanku, anak istriku meninggalkanku, orangtuaku meninggalkanku, semua orang yang kukenal melupakanku, mereka tak mau ikut mati bersamaku, mereka tak mau tahu lagi apa yang menimpaku dikuburku, mereka tak mau walau hanya menepiskan cacing yang menggerogoti tubuhku, mereka tak perduli lagi tubuhku membusuk sedikit demi sedikit, hingga tubuhku hancur dan berbau, hingga tubuhku menjadi tulang, lalu habis musnah menjadi tanah, kemana aku akan pergi, ruhku akan melayang memenuhi panggilan Penciptaku.
Wahai ALLAH, tak ada selain MU, Engkaulah yang akan menepiskan semua serangga yang mendekati tubuhku, akan Engkau jaga tubuhku yang masuk dalam perut Bumi, Engkau mendengar jeritan hatiku yang merindukan MU, maka dengarlah Wahai yang menciptakan harapan, wahai yang menciptakan segala kerinduan, wahai yang menciptakan keinginan untuk mengadu, kulontarkan kalimat yang kini hampir memecahkan kalbuku, aku tak mempunyai selain MU untuk mengadu, untuk menolong, untuk memberi, untuk diharapkan, untuk bergerak, untuk bernafas, untuk berucap, untuk bersuara, untuk mendengar, untuk melihat, untuk melangkah, untuk bergerak, untuk berfikir, untuk makan, untuk minum, untuk tersenyum, untuk bergembira, untuk segala galanya, selain MU, semua yang ku miliki, dan yang tak ku milki adalah milik MU, tubuhku milik MU, makananku milik MU, semua yang ku lihat milik MU, semua yang ku dengar Milik MU, semua yang ku ucapkan milik MU, semua langkahku milik MU, setiap nafasku milik MU, setiap detik jantungku milik MU, perasaanku milik MU, kerinduanku milik MU, harapanku milik MU, kesedihanku milik MU, kegembiraanku milik MU…
Alangkah indahnya wahai RABB, Karena Engkau memilikiku, Engkau menggenggam diriku, Engkau mengaturku, Engkau menjagaku, Engkau melindungiku, Engkau mengayomiku, Engkau melimpahkan kelembutan MU padaku, aku merindukan MU wahai ALLAH, Engkau memanggilku agar aku dekat kepada MU wahai ALLAH.
Wahai yang menciptakan cinta kasih di seluruh kalbu hamba NYA, Engkau menghendaki aku mencintai MU wahai ALLAH, wahai yang menciptakan lidah saling menyebut nama nama hamba NYA, Engkau menghendaki aku menyebut nama MU wahai ALLAH, wahai yang menciptakan segala yang indah, keindahan yang terlihat dan yang tak terlihat, keindahan yang terdengar dan tak terdengar, keindahan yang terucapkan dan tak terucapkan, keindahan yang terasa dan tak dapat dirasa, keindahan yang diketahui dan yang tak diketahui, keindahan yang tersaksikan dan yang tersembunyi, semua keindahan itu berasal dari keindahan MU wahai ALLAH, maka betapa indahnya Engkau, betapa lembutnya Engkau…
Maka Wahai Pencipta Keindahan, Wahai Pencipta Kelembutan, Wahai Pencipta Kasih sayang, sebagaimana Engkau perlihatkan keindahan yang ada pada makhluk MU, sebagaimana Engkau perlihatkan kelembutan yang ada pada makhluk MU, sebagaimana Engkau perlihatkan kasih sayang yang ada pada makhluk MU, maka perlihatkan padaku Keindahan MU wahai ALLAH, perlihatkan kelembutan MU wahai ALLAH, perlihatkan kasih sayang MU wahai ALLAH, walau hanya berupa harapan, walau hanya berupa sangkaan, walau hanya berupa khayalan, walau hanya berupa kerinduan, walau hanya berupa keinginan, walau hanya berupa airmata, walau hanya berupa pemberian, walau hanya berupa lamunan, walau hanya berupa kemudahan, walau hanya berupa pertolongan, asalkan aku mengetahui bahwa itu datang dari kelembutan MU, datang dari kasih sayang MU, datang dari keindahan MU…
Alangkah kecewa hamba yang hanya memiliki harapan, hamba yang hanya memiliki khayalan, hamba yang hanya memiliki lamunan, hamba yang hanya memiliki kerinduan, hamba yang hanya ingin dekat, hamba yang hanya mendambakan kelembutan, hamba yang hanya mendambakan ayoman, hamba yang hanya mendambakan kasih sayang, sedangkan modal semua harapanku hanyalah airmata, apakah ia harus dikecewakan oleh yang Maha tak mengecewakan…
Alangkah hancur perasaannya kalau kerinduannya ditolak oleh yang Maha tak menolak kerinduan, alangkah berkeping-kepingnya kecintaannya, bila keinginannya untuk dekat tertolak oleh yang Maha tak menolak hamba NYA yang ingin dekat, itu semua tak ada pada Dzat MU, itu semua tak ada dalam sifat MU, itu semua tak ada pada perbuatan MU, apalagi yang membuatku tertolak sedangkan Engkau yang Maha menerima, apalagi yang membuatku tersingkir sedangkan Engkau yang Maha merangkul, apalagi yang membuatku terjauhkan, sedangkan Engkaulah yang maha mendekatkan, salahkah aku merindukan MU, sedangkan Engkaulah yang menciptakan kerinduanku pada MU, salahkah aku menginginkan dekat pada MU, sedangkan Engkaulah yang menciptakan keinginanku untuk dekat kepada MU, salahkah aku merasa tenggelam dalam samudra Kelembutan MU, sedangkan Engkaulah yang menciptakan perasaa itu dihatiku…?
Wahai ALLAH, wahai yang menamakan diri NYA ALLAH, wahai yang menginginkan nama NYA dipanggil ALLAH, wahai yang menginginkan lidahku memanggil Dzat NYA dengan panggilan ALLAH, wahai yang menginginkan aku mengharapkan NYA dengan mengingat nama ALLAH, wahai yang menciptakan lidahku bergetar menyebut Nama ALLAH, wahai yang memberikan kemampuan pada jemariku menuliskan nama ALLAH, maka dengan kemauan MU ku sebut namamu ALLAH, dengan keinginan MU ku rindukan Engkau ALLAH, dengan keinginan MU aku ingin dekat kepada MU wahai ALLAH, salahkah aku berkeinginan, salahkah aku merindukan, salahkah aku ingin dekat, sedangkan semua getaran kalbuku itu adalah keinginan MU wahai ALLAH?
Maka sebagaimana Engkau jadikan cacing merangkak tanpa tangan dan kaki, maka jadikan aku merangkak kepada MU tanpa hambatan, sebagaimana Engkau jadikan anjing najis bertasbih mensucikan MU, maka jadikan aku pendosa hina yang mendambakan MU, sebagaimana Engkau jadikan air mengalir menjadi beku, maka jadikan harapanku mengalir kearah MU dan membeku dipintu MU, sebagaimana Engkau jadikan gunung batu menjadi debu, maka jadikan seluruh kesalahanku menjadi debu dihadapan Keagungan MU, sebagaimana Engkau jadikan bumi perkasa terinjak injak, maka jadikan hawa nafsuku terinjak injak kerinduanku kepada MU…
Sebagaimana Engkau jadikan Raja berwibawa terkalahkan dan terhinakan, maka jadikan kesombonganku terhinakan oleh kewibawaan MU, sebagaimana Engkau jadikan sesuatu yang bergerak menjadi diam, maka jadikan tubuhku yang bergerak berubah diam dari segala yang tak Engkau redhai, sebagaimana Engkau jadikan semua yang ada menjadi fana, maka jadikanlah gunung dosa ini fana dalam kelembutan MU, sebagaimana Engkau jadikan yang tak mungkin menjadi kepastian, maka jadikan semua ketidak mungkinanku untuk dekat menjadi janji kepastian…
ALLAHu RABBi…
Nukilan Indah :
Habib Munzir bin Fuad Almusawa
ALLAHu a`lam bisawab.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 5:16 AM 0 comments
Tugas Penuntut Ilmu
Secara Umum, dapat digariskan empat tugas seorang penuntut ilmu:
1 ) Memperbetulkan Niat
Perkara pertama yang perlu diambil perhatian oleh penuntu ilmu, ialah mempunyai keikhlasan niat demi untuk mencapai keredhaan ALLAH. Bukan untuk berbangga apabila digelarkan sebagai orang allim, atau tujuan mengumpulkan harta, pangkat atau yang seumpamanya.
Sabda RasulALLAH ShalALLAHu`alaihiwasalam :
"Sesiapa yang mempelajari ilmu kerana ALLAH, tidak mempelajari ilmu kerana inginkan harta dunia, tidak akan dia temui kecuali Syurga hari akhirat kelak..."
(Riwayat oleh Abd. Razak)
Cuma perlu di ingat bahawa, jika harta, pangkat dan yang seumpamanya datang kepada seorang alim, maka tidaklah menjadi kesalahan untuk menerima dan memanafaatkannya.
2 ) Berterusan Dalam Menuntut Ilmu
Ilmu adalah lautan yang tidak mempunyai pantai dan tepian. Maka usaha menuntut dan menambahkan ilmu hendaklah berlaku secara berterusan, tidak didalangi oleh peringkat-peringkat ijazah tertentu.
Firman ALLAH Azzawajalla:
"Katakanlah (wahai muhammad) tambahkan aku ilmu."
( surah Toha ayat 114 )
3 ) Sabar
Penuntut ilmu hendaklah sentiasa sabar dalam menempuh dugaan dan cabaran yang merintangi perjalanannya di dalam menuntut ilmu sama ada yang bersiafat fizikal mahupun spritual.
Tidak perlulah diceritakan di sini sejarah para sahabat dan ulama yang menempuh segala cabaran demi untuk menuntut ilmu.
4 ) Memuliakan Guru
Sabda RasulALLAH ShalALLAHu`alaihiwasalam:
"Bukan dari umatku orang yang tidak memuliakan orang tua dan mengasihi anak-anak muda kami dan tidak mempelajari daripada orang-orang alim."
(Riwayat Abu Daud)
Saya tidak bertujuan untuk menghuraikan hak seorang alim/guru ytang perlu ditunaikan oleh muridnya di dalam artikel ini cuma dicadangkan agar kita mengambil sedikit dari masa kita untuk melihat kembali perkara ini, semoga segala ilmu yang kita tuntut mendapat keredhaan ALLAH Azzawajalla.
Akhlak Penuntut Ilmu
1 ) Merasakan Tanggungjawab Ilmu
Diriwayatkan Daripada Muaz bin Jabal dia berkata RasulALLAH ShalALLAHu`alaihiwasalam bersabda:
"Tidak akan mara seseorang hamba di hari Akhirat melainkan telah ditanya mengenai 4 perkara: Berkenaan Umurnya ke mana yang telah dia habiskan. Berkenaan dengan Waktu mudanya apa yang telah dia lakukan. Berkenaan dengan hartanya dari mana diperolehinya dan ke mana dia belanjakan. Dan berkenaan dengan ilmu apa yang telah perbuat dengannya."
(Riwayat oleh at-Tabarani dengan isnad yang sahih)
2 ) Menjaga Amanah Ilmiah
Sabda RasulALLAH ShalALLAHu`alaihiwasalam:
"Berilah nasihat pada ilmu, Sesungguhnya khianat seseorang daripada kamu terhadap ilmu adalah lebih dahsyat daripada khianatnya terhadap hartanya, Dan sesungguhnya ALLAH akan bertanya kepada kamu pada hari kiamat."
(Riwayat At-Tabarani)
Di antara yang termasuk dalam daerah amanah ilmu adalah beberapa perkara berikut.
- Menasabkan atau menyandarkan pendapat dan fikrah (buah fikiran) kepada Tuannya.
- Menyampaikan ilmu yang diketahui, dan tidak malu untuk mengatakan "tidak tahu" jika dia tidak mengetahuinya.
3 ) Tawadduk
Para Ilmuan yang menyedari bahawa ilmu adalah lautan yang tidak bertepi tidak akan merasa sombong dan bangga dengan apa yang ada pada mereka. Bahkan selagi bertambah ilmu di dada, semakin bertambah sifat tawadduk.
Firman ALLAH Azzawajalla:
"Tidak diberi kepada kamu ilmu kecuali sedikit sahaja."
( Surah al-Isra' ayat 85 )
4 ) Mulia Diri (Al-Izzah)
Para ilmuan hendaklah merasa mulia diri tidak merendahkan diri apabila berhadapan dengan pemerintah, golongan bangsawan, golongan kaya-raya dan yang seumpamanya,
Firman ALLAH Azzawajalla:
"Kekuatan itu hanyalah kepada ALLAH, bagi RasulNya dan bagi orang-orang mukmin, tetapi orang-orang munafik itu tidak mengetahui."
( Surah al-Munafiqun ayat 8 )
"Barangsiapa yang menghendaki kemuliaan, maka bagi ALLAH-lah kemuliaan itu semuanya."
( Surah Fathiir ayat 10 )
5 ) Beramal Dengan Apa Yang Dipelajari
Firman ALLAH Azzawajalla:
"Mengapa kamu menyuruh orang lain (mengerjakan) kebajikan, sedangkan kamu sendiri melupakan diri (kewajiban)mu sendiri padahal kamu mambaca Al-Kitab (Taurat)? Maka tidakkah kamu berfikir?"
( Surah al-Baqarah ayat 44 )
6 ) Sentiasa Berusaha Untuk Menyampaikan Ilmu
Firman ALLAH Azzawajalla:
"Dan (ingatlah) ketika ALLAH mengambil janji dari orang-orang yang telah diberi kitab (iaitu):"Hendalah kamu menerangkan isi kitab itu kepada manusia, dan janganlah kamu menyembunyikannya", lalu mereka melemparkan janji itu ) ke
belakang punggung mereka dan mereka menukarkannya dengan harga yang sedikit, Amatlah buruk tukaran mereka terima."
( Surah Ali Imran ayat 187 )
Oleh: Azmi Hashim
Suara Persatuan Ulama' Online
ALLAHu a`lam bisawab.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 5:15 AM 0 comments
Wednesday, October 14, 2009
Hαti ♥ Bєrhαti-hαti
بســــم الله الرحمان الرحيم
الحمد لله رب العالمين حمداً يوافى نعمه ويكافئ مزيده
اللهم صل على سيدنا محمد عبدك
ورسولك النبي الأمي
وعلى آله وصحبه وسلم
- Selawat Ummi
اللهم أنت ربي لا إله إلا أ نت خلقتني وأنا عبدك
وأنا على عهدك ووعدك ما استطعت
أعوذ بك من شر ما صنعت
أبوء لك بنعمتك علي وأبوء لك بذنبي
فاغفر لي فإنه لا يغفر الذنوب إلا أنت
- Sayyidul Istighfar
"Ketahuilah, wahai Saudara² sekalian, moga² ALLAH تعالى Menggolongkan kita sekalian ke dalam kumpulan orang² yang lurus dan bersih naluri nya lahir dan batin serta mengikuti jejak langkah dan kepercayaan yang hak (benar) dan mengamalkan dengan nya. (Amiin ALLAHumma amiin) Bahwasa nya antara perkara² yang terpenting atas setiap Mu`min, ialah memerhati dan mengamat-amati gerak-geri hati dan segala anggota tubuh, mengawas kedua nya, berusaha sesungguh yang boleh untuk memelihara dan menahan nya dari terjerumus ke dalam perbuatan yang dimurkai ALLAH dan dibenciNYA sambil menganjur dan menggalakkan nya untuk berkecimpung ke dalam perbuatan² yang diredhai dan dikasihiNYA.
ALLAH سبحانه وتعالى telah berfirman :
"Sesungguh nya pendengaran, penglihatan dan hati (kebatinan), semua itu akan dipertanggungjawabkan." - al-Isra` ayat 36
Hati dan semua anggota badan itu merupakan ni`mat² utama ALLAH bagi hamba²NYA. Barangsiapa yang menggunakan nya untuk ketaatan terhadap ALLAH تعالى, dan menyerikan nya dengan perbuatan² yang menimbulkan Kasih-SayangNYA, itu bermakna ia telah mensyukuri ALLAH تعالى, dan memelihara kehormatan anggota² itu serta meletakkan perkhidmatan nya pada tempat nya yang baik, kerana itulah anggota² itu dicipta dan dijadikan oleh Tuhan. Sebab itu, maka ia akan memperolehi pahala orang² yang bersyukur kepada ALLAH تعالى serta balasan orang² yang berbuat kebajikan terhadapNYA, kerna ALLAH سبحانه وتعالى tidak akan mensia²kan pahala orang² yang berbuat baik.
Barangsiapa membiarkan hati nya serta seluruh anggota nya melanggar larang² ALLAH تعالى, mencuai dan mensia²kan perintah²NYA, tidak pernah menunaikan nya, maka ia telah mengkufuri ni`mat ALLAH pada anggota² itu, dan kerna itu ia harus membayar denda dan menerima siksaan ALLAH تعالى. Di hari Kiamat kelak semua anggota² itu akan menjadi saksi di hadapan ALLAH تعالى atas segala maksiat yang dikerjakan dahulu di dunia.
Firman ALLAH تعالى :
"Di hari lidah, tangan dan kaki mereka menjadi saksi terhadap segala perbuatan yang telah mereka kerjakan." - an-Nur ayat 24
FirmanNYA lagi :
"Pada hari itu, KAMI Tutup mulut mereka, akan tetapi tangan mereka akan berkata² kepada KAMI, dan kaki mereka akan menjadi saksi terhadap apa yang mereka lakukan." - Yasin ayat 65
Adapun peranan hati itu, maka ia sebagai kepala anggota dan ketua nya. Pada nya tergantung segala baik atau buruk nya gerak-geri anggota. Nabi صلى الله عليه وسلم telah bersabda :
"Ketahuilah, bahwasa nya di dalam tubuh itu ada seketul daging, jika baik daging itu, baiklah seluruh tubuh itu. Jika buru, buruk pula seluruh tubuh. Ia tiada lain melainkan hati."
Adapun anggota² yang dimaksudkan itu ialah tujuh kesemua nya; iaitu mata, telinga, lidah, perut, kemaluan, tangan dan kaki." - Dari kitab "Nasihat Agama Dan Wasiat Iman" karangan al-Imam al-Qutub al-Habib `AbduLlah ibn `Alawi al-Haddad dengan terjemahan oleh al-Habib Ahmad ibn Muhammad Semait رضي الله تعالى عنهم
Wahai ALLAH, Tuhan yang telah Menciptakan kami, kami Berlindung kepadaMU dari keburukan
yang kami lakukan, dan kami Berlindung kepadaMU, dari segala sesuatu yang mengundang KemurkaanMU baik dari perkataan, perbuatan, niat serta keyakinan,
sesungguh nya Engkau Maha Mendengar lagi Maha Dekat...
وصلى الله على سيدنا محمد وعلى آله وصحبه أجمعين
سبحان ربك رب العزة عما يصفون
وسلام على المرسلين والحمد لله رب العالمين
بارك الله فيكم وجزاكم الله خير الجزاء
والله تعالى أعلم بالصواب
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 3:36 PM 0 comments
.:Di Atas Sejadah Cinta:.
DiriMu ada
Dalam setiap langkah manusia
Janganlah pernah ragukan kuasaNya
Dalam kehidupan
Manusia terkadang dicuba
Selalu kau dapat memohon padaNya
Allah tempat ku mengadu
Allah tempat ku bersujud
Allah rahmatMu menerangi jalan hidupku
Andai kau sedar
Dirimu ciptaan Yang Kuasa
Mengapa senantiasa menjauh dariNya
Allah tempat ku mengadu
Allah tempat ku bersujud
Allah rahmatMu menerangi jalan hidupku
Ajarkanlah aku mengenal cintaMu ya Allah...
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 3:27 PM 0 comments
Saturday, August 1, 2009
Lec2 - Authentication and Cryptography
Authentication
Computer security authentication means verifying the identity of a user logging onto a network. Passwords, digital certificates, smart cards and biometrics can be used to prove the identity of the user to the network. Computer security authentication includes verifying message integrity, e-mail authentication and MAC (Message Authentication Code), checking the integrity of a transmitted message. There are human authentication, challenge-response authentication, password, digital signature, IP spoofing and biometrics.
Password
A password is a secret word or string of characters that is used for authentication, to prove identity or gain access to a resource (Example: An access code is a type of password). The password must be kept secret from those not allowed access. The use of passwords is known to be ancient. Sentries would challenge those wishing to enter an area or approaching it to supply a password or watchword. Sentries would only allow a person or group to pass if they knew the password. In modern times, user names and passwords are commonly used by people during a log in process that controls access to protected computer operating systems, mobile phones, cable TV decoders, automated teller machines (ATMs), etc. A typical computer user may require passwords for many purposes: logging in to computer accounts, retrieving e-mail from servers, accessing programs, databases, networks, web sites, and even reading the morning newspaper online.
To choose a good password
A good password is one that's hard to guess, yet easy to remember. So here are the top 10 ways to choose a password, in roughly increasing difficulty. If you don't use any of the first 5, you're well on your way. The stats are very rough estimates (for comparison purposes, an 8-character password is used for most calculations):
- Default (same as none):
- Many programs and services assign a default password . Change this to a new password immediately.
- examples: password, superuser
- 10 Common passwords:
- god, love, lust, money, private, qwerty, secret, sex, snoopy, & (surprise!) password
- Personal info:
- your name, initials, location (zip code), birthday, pets, license plate
- family/friend's names (including maiden), locations, birthdays, pets
- word/number combinations of any of the above
- Ego-related; examples: guru, master, wizard
- Favorite: Music (group names, albums), Fiction/Nonfiction/Comic books/characters, Movie/TV/Cartoon characters & titles
- Dumb Hollywood movie-people think all passwords are of this variety
- Categories:
- Double-words; examples: kittykitty, johnjohn
- Funny/nonsense/jargon words; examples: wassup, bzzzzz, foobar
- Insults; examples: biteme, eatdirt
- Keyboard sequences; examples: asdfg, qweasd, poiqwe
- Obscene words; examples: (use your imagination)
- Passwords based on host name (for people with lots of passwords)
- for example, if the system is named 'cat' an obvious password is catpass
- Reversals; examples: terces, wordpass, nhojnhoj
- Dictionary & Foreign Language words:
- If you can find your word here, it's not a very good password.
- Common Passwords - Various Languages
- Dan Klein - Browsable and categorized lists of English words
- DEC Collection - compressed lists of common English words
- stats: There's 200,000+ words in the English language (most people use around 10,000-40,000). As a guesstimate, there's some 32,000 8-letter words/phrases.
- For some word lists, see The Electronic Alveary
- Mixed-Case Dictionary Words (alternating UPPER-lower case letters)
- examples: paSSworD, PLaceBO
- stats: If a word has 2 letters, there's 4 (22) ways to capitalize it (at, At, aT, AT). If a word has 8 letters, there's 256 ways. Similar combinations (2letters) apply to each word in the dictionary. Guesstimate: There's around 32,000 8-letter words, which gives 8 million (32,000 x 256) mixed-case 8-letter passwords
- Mixed-case Word with Number(s)
- examples: 9fiNgeRS, loVELy68
- stats: Tacking on a number from 0-9 before or after a word gives 20 more variations to the password. Using 00-99 before or after the word, gives 200 variations. Guesstimate: there's some 19,000 6-letter words, and 243 million variations (19,000 x 64 x 200) of 6-letter-word 2-number passwords.
- Mixed-case Word(s)/Letter(s)
- Combining words and/or extra letters
- examples: GUessTHis, BiKeFisH
- stats: We're talking pretty big numbers here. Around 53 trillion (528) 8-letter mixed-case passwords (i.e. aaaaaaaa, aaaaaaaA, aaaaaaAa, ..., ZZZZZZZZ)
- Mixed-case Words/Numbers/Letters
- examples: No50WaY2, puT863MoX
- variant: Hacker/IRC/License-plate jargon
- examples: H4x0rD00dZ, UR2good4Me, FXR1stR8
- stats: OK, my mind's swimming, there's somewhere around 218 trillion (628) 8-letter/number passwords
- It takes an average of 5 seconds to crack this kind of password on a Windows machine; considerably longer on BSD or Linux.
- Random characters
- examples: qs3UIs82, k38#0J$dA
- note: some programs and services only allow letters and numbers, some include dashes ('-'); the best allow any character
- stats: Assuming 94 'type-able' characters, there's 6 gazillion (948 = 6.1 quadrillion [US]) different 8-character passwords. There's not as many 7-character passwords, but there's some 9-character ones still available, if you hurry.
In general:
- No password is uncrackable.
- The best you can do is make it difficult and non-trivial to determine your password.
- What's the worst password? The one you've forgotten.
- Whatever method you choose, it's a good idea to change your password often.
- The more important the password, the more often it should be changed.
- Why? If someone is attempting a brute-force attack on your password, the hope is that you're changing it to something they've already tried and found to be wrong.
- The longer the password, the harder it is to 'guess.'
- note: many systems limit passwords to 8 characters.
- Some clever people are foregoing brute-force hacks (e.g. dictionary attacks), in favor of 'social engineering' to obtain passwords.
- If somebody calls or emails, requesting your password, it's a dumb idea to give it to them.
- Of course nobody would sticky-note a password to their monitor, or under a keyboard
The concept of securing messages through cryptography has a long history. Indeed, Julius Caesar is credited with creating one of the earliest cryptographic systems to send military messages to his generals.
Throughout history, however, there has been one central problem limiting
widespread use of cryptography. That problem is key management. In
cryptographic systems, the term key refers to a numerical value used by an algorithm
to alter information, making that information secure and visible only to individuals
who have the corresponding key to recover the information. Consequently, the term
key management refers to the secure administration of keys to provide them to users
where and when they are required.
Historically, encryption systems used what is known as symmetric cryptography.
Symmetric cryptography uses the same key for both encryption and decryption.
Using symmetric cryptography, it is safe to send encrypted messages without fear of
interception (because an interceptor is unlikely to be able to decipher the message);
however, there always remains the difficult problem of how to securely transfer the
key to the recipients of a message so that they can decrypt the message.
A major advance in cryptography occurred with the invention of public-key
cryptography. The primary feature of public-key cryptography is that it removes the
need to use the same key for encryption and decryption. With public-key
cryptography, keys come in pairs of matched “public” and “private” keys. The
public portion of the key pair can be distributed in a public manner without
compromising the private portion, which must be kept secret by its owner. An
operation (for example, encryption) done with the public key can only be undone
with the corresponding private key.
Prior to the invention of public-key cryptography, it was essentially impossible to
provide key management for large-scale networks. With symmetric cryptography, as
the number of users increases on a network, the number of keys required to provide
secure communications among those users increases rapidly. For example, a network
of 100 users would require almost 5000 keys if it used only symmetric cryptography.
Doubling such a network to 200 users increases the number of keys to almost
20,000. Thus, when only using symmetric cryptography, key management quickly
becomes unwieldy even for relatively small-scale networks.
Encryption and digital signature
To better understand how cryptography is used to secure electronic communications,
let’s look at a process we are all familiar with: writing and sending a check.
Securing the electronic version
The simplest electronic version of the check can be a text file, created with a word
processor, asking your bank to pay someone a specific sum. However, sending this
check over an electronic network poses several security problems:
- • since anyone could intercept and read the file, you need confidentiality.
- • since someone else could create a similar counterfeit file, the bank needs to
authenticate that it was actually you who created the file.
- • since you could deny creating the file, the bank needs non-repudiation.
- • since someone could alter the file, both you and the bank need data
integrity.
To overcome these issues, Entrust performs a number of steps hidden behind a
simple user interface. The first step is to “sign” the check with a digital signature.
The process of digitally signing starts by taking a mathematical summary (called a hash code) of the check. This hash code is a uniquely-identifying digital fingerprint of the check. If even a single bit of the check changes, the hash code will dramatically change. The next step in creating a digital signature is to sign the hash code with your private key. This signed hash code is then appended to the check. How is this a signature? Well, the recipient of your check can verify the hash code sent by you, using your public key. At the same time, a new hash code can be created from the received check and compared with the original signed hash code. If the hash codes match, then the recipient has verified that the check has not been altered. The recipient also knows that only you could have sent the check because only you have the private key that signed the original hash code.
Confidentiality and encryption
Once the electronic check is digitally signed, it can be encrypted using a high-speed mathematical transformation with a key that will be used later to decrypt the document. This is often referred to as a symmetric key system because the same key is used at both ends of the process.
As the check is sent over the network, it is unreadable without the key. The next challenge is to securely deliver the symmetric key to the bank. Public-key cryptography for delivering symmetric keys Public-key encryption is used to solve the problem of delivering the symmetric encryption key to the bank in a secure manner. To do so, you would encrypt the symmetric key using the bank’s public key. Since only the bank has the corresponding private key, only the bank will be able to recover the symmetric key and decrypt the check.
Public Key InfrastructureThe Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a set of hardware, software, people, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, store, distribute, and revoke digital certificates.
In cryptography, a PKI is an arrangement that binds public keys with respective user identities by means of a certificate authority (CA). The user identity must be unique for each CA. The binding is established through the registration and issuance process, which, depending on the level of assurance the binding has, may be carried out by software at a CA, or under human supervision. The PKI role that assures this binding is called the Registration Authority (RA) . For each user, the user identity, the public key, their binding, validity conditions and other attributes are made unforgettable in public key certificates issued by the CA. The term trusted third party (TTP) may also be used for certificate authority (CA).
The term PKI is sometimes erroneously used to denote public key algorithms, which do not require the use of a CA.
RSA
The RSA algorithm involves three steps: key generation, encryption and decryption.
RSA involves a public key and a private key. The public key can be known to everyone and is used for encrypting messages. Messages encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted using the private key. The keys for the RSA algorithm are generated the following way:
- Choose two distinct prime numbers p and q.
- Compute n = pq.
- n is used as the modulus for both the public and private keys
- Compute the totient:
 .
. - Choose an integer e such that
 , and e and
, and e and  share no divisors other than 1 (i.e. e and
share no divisors other than 1 (i.e. e and  are coprime).
are coprime). - Determine d (using modular arithmetic) which satisfies the congruence relation
 .
. - Stated differently, ed − 1 can be evenly divided by the totient (p − 1)(q − 1).
- This is often computed using the Extended Euclidean Algorithm.
- d is kept as the private key exponent.
The public key consists of the modulus n and the public (or encryption) exponent e. The private key consists of the modulus n and the private (or decryption) exponent d which must be kept secret.
Notes on some variants:
- For efficiency the following values may be precomputed and stored as part of the private key:
- p and q: the primes from the key generation,
 and
and  ,
,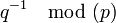 .
.
Alice transmits her public key (n,e) to Bob and keeps the private key secret. Bob then wishes to send message M to Alice.
He first turns M into an integer 0 < m < n by using an agreed-upon reversible protocol known as a padding scheme. He then computes the ciphertext c corresponding to:
This can be done quickly using the method of exponentiation by squaring. Bob then transmits c to Alice.
Alice can recover m from c by using her private key exponent d by the following computation:
Given m, she can recover the original message M by reversing the padding scheme.
The above decryption procedure works because:
 .
.
Now, since 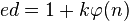 ,
,
 .
.
The last congruence directly follows from Euler's theorem when m is relatively prime to n. By using the Chinese remainder theorem it can be shown that the equations hold for all m.
This shows that we get the original message back:
A working example
Here is an example of RSA encryption and decryption. The parameters used here are artificially small, but one can also use OpenSSL to generate and examine a real keypair.
- Choose two prime numbers
- p = 61 and q = 53
- Compute n = pq
- Compute the totient

- Choose e > 1 coprime to 3120
- e = 17
- Compute d such that
 e.g., by computing the modular multiplicative inverse of e modulo
e.g., by computing the modular multiplicative inverse of e modulo  :
: - d = 2753
- since 17 · 2753 = 46801 and mod (46801,3120) = 1 this is the correct answer.
The public key is (n = 3233, e = 17). For a padded message m the encryption function is:
The private key is (n = 3233, d = 2753). The decryption function is:
For example, to encrypt m = 123, we calculate
To decrypt c = 855, we calculate
 .
.
Posted by ~Nurul Ain~ at 8:49 AM 0 comments